Online NCP-MCI-6.10 Practice TestMore Nutanix Products >
Free Nutanix NCP-MCI-6.10 Exam Dumps Questions
Nutanix NCP-MCI-6.10: Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Infrastructure (NCP-MCI v6.10)
- Get instant access to NCP-MCI-6.10 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the Nutanix Certified Professional - Multicloud Infrastructure (NCP-MCI v6.10) exam right now using our Nutanix NCP-MCI-6.10 exam package, which includes Nutanix NCP-MCI-6.10 practice test plus an Nutanix NCP-MCI-6.10 Exam Simulator.
- The best online NCP-MCI-6.10 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
A company is evaluatingNutanix Disaster Recovery (DR)to protect multiplebusiness- critical applications. Some applications are built using a3-tier architectureand have interdependencies.
Afterfailover, the VM'sstatic IP address is retained, butDNS configuration is lost.
How should an administrator proceed to resolve this issue?
Correct Answer:B
Duringfailover in Nutanix Disaster Recovery, VMs retain theirstatic IPsbut maylose DNS settingsif the network configuration at the DR site is different from the primary site.
✑ Option B (Create custom in-guest scripts) is correct:
✑ Option A (Self-Service Restore) is incorrect:
✑ Option C (nncli tool) is incorrect:
✑ Option D (Configure a Protection Domain) is incorrect:
References:
✑ Nutanix Disaster Recovery Guide Failover Automation and Network Configuration
✑ Nutanix Bible VM Recovery and IP Management in DR Scenarios
✑ Nutanix KB Preserving DNS Settings in Disaster Recovery
Question 2
An administrator has been tasked with justifyingwhy Nutanix Disaster Recoverywas chosen for amulti-tier application spanning multiple business units.
What is the most efficient way to organize and manage the workloads?
Correct Answer:B
Nutanix Categories allow administrators to group related VMs, making Disaster Recovery (DR) planning easier.
✑ Option B (Utilize Categories to organize VMs in Recovery Plans) is correct:
✑ Option A (Naming schema) is incorrect:
✑ Option C (1:10 Recovery Plan to VMs) is incorrect:
✑ Option D (RESTful APIs) is incorrect:
References:
✑ Nutanix Disaster Recovery Guide Using Categories for DR Management
✑ Nutanix KB Organizing VMs for Disaster Recovery Planning
Question 3
Which predefined view in Prism Central??s Intelligent Operations should be used to determine which VM is consuming excessive resources and causing performance issues for others?
Correct Answer:C
TheBully VMs List (Option C)in Prism Central??sIntelligent OperationsidentifiesVMs consuming excessive CPU, memory, or storage, which negatively affects other VMs.
✑ Option A (Inactive VMs List)is used foridentifying unused VMsbut does not detect performance issues.
✑ Option B (Overprovisioned VMs List)helps identifyVMs with excessive allocated resources, but it does not focus on live performance impact.
✑ Option D (Constrained VMs List)highlightsVMs suffering from resource contention, not those causing it.
References:
✑ Nutanix Prism Central Intelligent Operations and Performance Tuning
✑ Nutanix KB Identifying and Managing Resource-Hogging VMs
Question 4
Refer to Exhibit: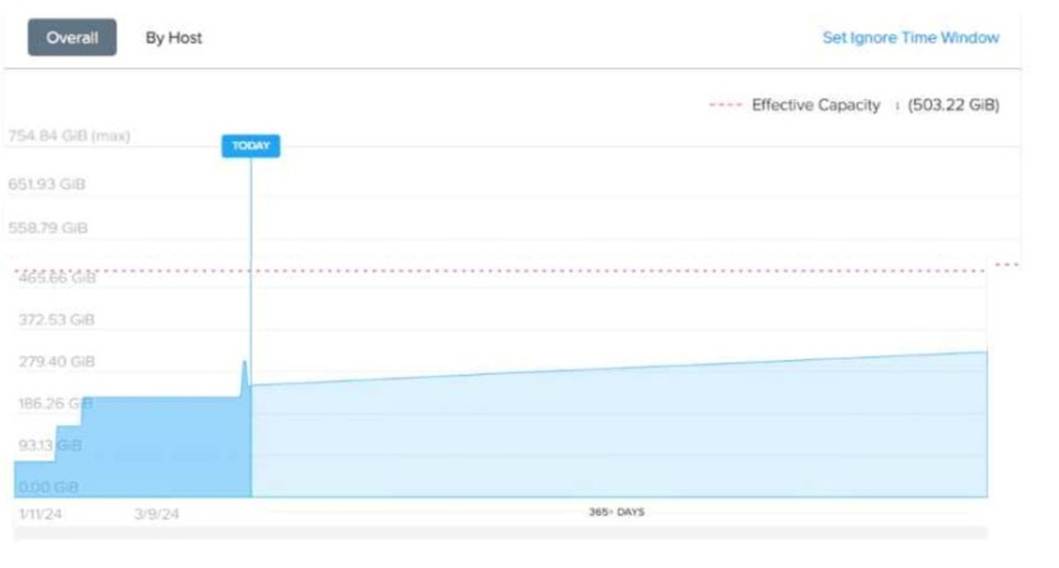
An administrator is looking at thememory cluster runway diagramas shown in exhibit,in Prism Central. The environment hasthree hostswith the following configuration:
✑ CPU: 2x Intel Xeon Gold (8 cores, 2.6 GHz)
✑ RAM: 256 GB per host
✑ Storage: SSDs and HDDs
TheIntelligent Operations featurehas been active forone month, but no further configurations were applied.
What does the dotted red line mean?
Correct Answer:D
hePrism Central Memory Cluster Runway Diagramprovides insights into memory usage trends, predicting how long the cluster can sustain workloads before exhausting resources.
✑ Thesolid blue arearepresents theactual memory consumption over time.
✑ Thedotted red linerepresents theeffective memory capacity limitbased on the cluster's current configuration.
Analyzing the Dotted Red Line
Thedotted red line is labeled "Effective Capacity: 503.22 GiB", which means:
✑ It is the totalusable memory capacityin the cluster after consideringhypervisor overhead, redundancy settings, and failover capacity.
✑ This value isnot a hard limitbut an indication ofthe available memory before potential performance issues occur.
Evaluating the Answer Choices
(A) It is the default trend analysis static threshold that can be manually set.(Incorrect
)
✑ Thedotted red line is not a static thresholdthat an administrator can manually configure.
✑ Trend analysis in Prism isdynamicand based on workload history and projections.
(B) It is the maximum memory the administrator can assign to VMs.(Incorrect)
✑ Administrators canoversubscribememory beyond the dotted red line if memory overcommitment is enabled.
✑ However, oversubscribing memory beyondeffective capacitymay impact performance.
(C) It is the calculated memory oversubscription limit for currently running VMs.( Incorrect)
✑ The dotted red linedoes not represent oversubscription limits.
✑ Memory oversubscription depends onhypervisor memory ballooning, compression, and swappingmechanisms, which are not directly shown here.
(D) It is the usable capacity based on cluster configuration options.(Correct Answer)
✑ Thedotted red line (503.22 GiB)represents theactual usable memory availablein the cluster after factoring in system overhead.
✑ This value is determined by:
Multicloud Infrastructure References & Best Practices
✑ Prism Central??s "Runway" featureprovidesAI-driven trend analysisfor memory, CPU, and storage capacity.
✑ Theeffective capacity limithelps administrators makeproactive scaling decisionsbefore resources become critical.
✑ To increase thememory runway, administrators can:
Question 5
An administratorwants to ensure that VMscan bemigrated and restarted on another nodein the event of asingle-host failure.
What action should be taken in Prism Element to meet this requirement?
Correct Answer:B
To ensureVM high availability (HA) in the event of a node failure, the administrator mustenable HA Reservation (Option B)in Prism Element.
✑ High Availability (HA) in Nutanix ensures that VMs restart on another available node if the host they are running on fails.
✑ Option A (Redundancy Factor 3)affectsstorage redundancy, not VM failover.
✑ Option C (Protection Domains)is related todisaster recovery (DR), not local HA failover.
✑ Option D (RF1 Storage Container)would reduce fault tolerance and is not recommended for production environments.
References:
✑ Nutanix Prism Element Guide Configuring HA Reservation
✑ Nutanix Bible High Availability (HA) and Failover
✑ Nutanix Support KB VM Recovery with HA Enabled
Question 6
When expanding acluster, what is required toautomatically discover new nodes?
Correct Answer:D
Nutanix uses IPv4 multicast for automatic node discovery and cluster expansion.
✑ Option D (IPv4 multicast must be allowed) is correct:
✑ Option A (Hypervisor version must match) is incorrect:
✑ Option B (IPv6 multicast) is incorrect:
✑ Option C (AOS version must match) is incorrect:
References:
✑ Nutanix Best Practices Cluster Expansion & Auto-Discovery
✑ Nutanix KB Why Nutanix Requires IPv4 Multicast for Node Discovery