Online 100-150 Practice TestMore Cisco Products >
Free Cisco 100-150 Exam Dumps Questions
Cisco 100-150: Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking
- Get instant access to 100-150 practice exam questions
- Get ready to pass the Cisco Certified Support Technician (CCST) Networking exam right now using our Cisco 100-150 exam package, which includes Cisco 100-150 practice test plus an Cisco 100-150 Exam Simulator.
- The best online 100-150 exam study material and preparation tool is here.
Question 1
An engineer configured a new VLAN named VLAN2 for the Data Center team. When the team tries to ping addresses outside VLAN2 from a computer in
VLAN2, they are unable to reach them. What should the engineer configure?
Correct Answer:C
When devices within a VLAN are unable to reach addresses outside their VLAN, it typically indicates that they do not have a configured path to external networks. The engineer should configure a default gateway for VLAN2. The default gateway is the IP address of the router??s interface that is connected to the VLAN, which will route traffic from the VLAN to other networks12.
References :=
•Understanding and Configuring VLAN Routing and Bridging on a Router Using the IRB Feature
•VLAN 2 not able to ping gateway - Cisco Community
=========================
•VLANs: Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) logically segment network traffic to improve security and performance. Devices within the same VLAN can communicate directly.
•Default Gateway: For devices in VLAN2 to communicate with devices outside their VLAN, they need a default gateway configured. The default gateway is typically a router or Layer 3 switch that routes traffic between different VLANs and subnets.
•Additional VLAN: Not needed in this scenario as the issue is related to routing traffic outside VLAN2, not creating another VLAN.
•Default Route: While a default route on the router may be necessary, the primary issue for devices within VLAN2 is to have a configured default gateway.
•Static Route: This is used on routers to manually specify routes to specific networks but does not address the need for a default gateway on the client devices.
References:
•Cisco VLAN Configuration Guide: Cisco VLAN Configuration
•Understanding and Configuring VLANs: VLANs Guide
Question 2
Which standard contains the specifications for Wi-Fi networks?
Correct Answer:C
The IEEE 802.11 standard contains the specifications for Wi-Fi networks. It is a set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication in various frequencies, including but not limited to 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz1. This standard is maintained by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and is commonly referred to as Wi-Fi. The standard has evolved over time to include several amendments that improve speed, range, and reliability of wireless networks.
References :=
•The Most Common Wi-Fi Standards and Types, Explained
•802.11 Standards Explained: 802.11ax, 802.11ac, 802.11b/g/n, 802.11a
•Wi-Fi Standards Explained - GeeksforGeeks
=========================
Question 3
DRAG DROP
Move the MFA factors from the list on the left to their correct examples on the right. You may use each factor once, more than once, or not at all.
Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.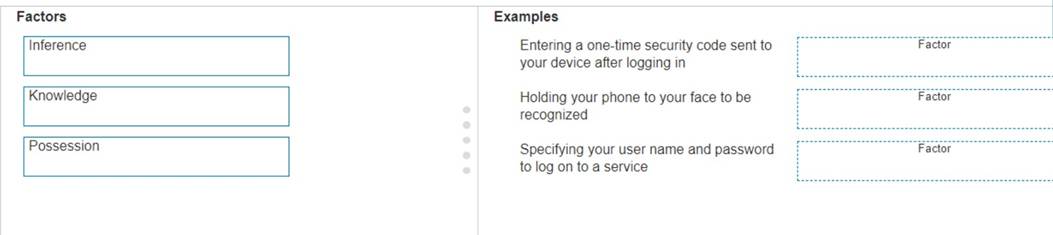
Solution:
The correct matching of the MFA factors to their examples is as follows:
✑ Entering a one-time security code sent to your device after logging in: Possession
✑ Holding your phone to your face to be recognized: Inherence
✑ Specifying your user name and password to log on to a service: Knowledge Here??s why each factor matches the example:
✑ Possession: This factor is something the user has, like a mobile device. A one- time security code sent to this device falls under this category.
✑ Inherence: This factor is something the user is, such as a biometric characteristic.
Facial recognition using a phone is an example of this factor.
✑ Knowledge: This factor is something the user knows, like a password or PIN. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances security by requiring two or more of these factors to verify a user??s identity before granting access.
✑ Entering a one-time security code sent to your device after logging in.
✑ Holding your phone to your face to be recognized.
✑ Specifying your username and password to log on to a service.
✑ Possession Factor: This involves something the user has in their possession.
Receiving a one-time security code on a device (e.g., phone) is an example of this.
✑ Inference Factor (Inherence/Biometric): This involves something inherent to the user, such as biometric verification (e.g., facial recognition or fingerprint scanning).
✑ Knowledge Factor: This involves something the user knows, such as login credentials (username and password).
References:
✑ Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Explained: MFA Guide
✑ Understanding Authentication Factors: Authentication Factors
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A
Question 4
HOTSPOT
Computers in a small office are unable to access companypro.net. You run the ipconfig command on one of the computers. The results are shown in the
exhibit.
You need to determine if you can reach the router.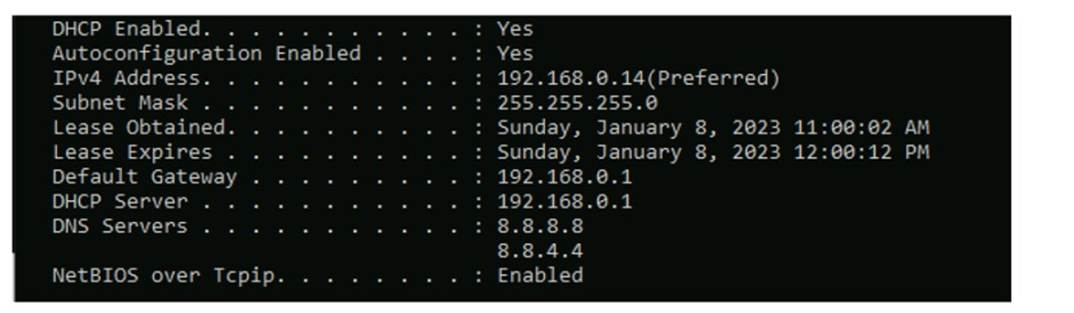
Which command should you use? Complete the command by selecting the correct options from each drop-down lists.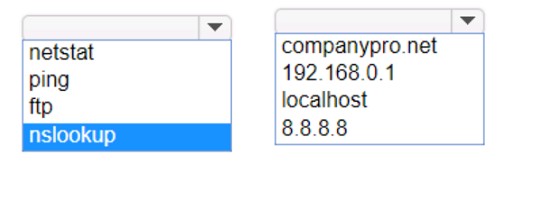
Solution:
To determine if you can reach the router, you should use the ping command followed by the IP address of the router. The ping command is a network utility used to test the
reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
The Default Gateway in the ipconfig results is typically the router??s IP address in a home or small office network. In this case, the Default Gateway is 192.168.0.1, which is the address you would ping to check connectivity to the router.
References :=
✑ How to Use the Ping Command
✑ Testing Network Connectivity with the Ping Command
=========================
To determine if you can reach the router, you should use the ping command with the IP address of the router.
✑ Command: ping
✑ Target: 192.168.0.1 So, the completed command is:
✑ ping 192.168.0.1
Step by Step Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation:
✑ ping: The ping command sends ICMP Echo Request messages to the target IP address and waits for an Echo Reply. It is commonly used to test the reachability of a network device.
✑ 192.168.0.1: This is the IP address of the default gateway (the router) as shown in the ipconfig output. Pinging this address will help determine if the computer can communicate with the router.
References:
✑ Using the ping Command: ping Command Guide
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A
Question 5
DRAG DROP
Move each protocol from the list on the left to the correct TCP/IP model layer on the right. Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct match.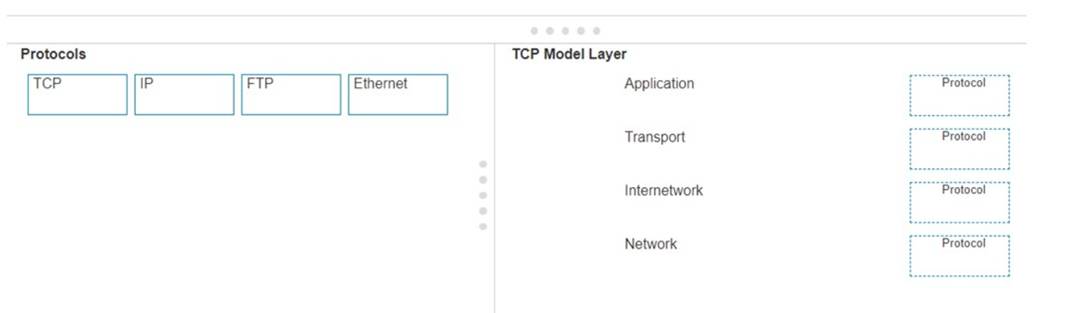
Solution:
Here??s how each protocol aligns with the correct TCP/IP model layer:
✑ TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): This protocol belongs to the Transport layer, which is responsible for providing communication between applications on different hosts1.
✑ IP (Internet Protocol): IP is part of the Internetwork layer, which is tasked with routing packets across network boundaries to their destination1.
✑ FTP (File Transfer Protocol): FTP operates at the Application layer, which supports application and end-user processes. It is used for transferring files over the network1.
✑ Ethernet: While not a protocol within the TCP/IP stack, Ethernet is associated with the Network Interface layer, which corresponds to the link layer of the TCP/IP model and is responsible for the physical transmission of data1.
The TCP/IP model layers are designed to work collaboratively to transmit data from one layer to another, with each layer having specific protocols that perform functions necessary for the data transmission process1.
✑ TCP:
✑ IP:
✑ FTP:
✑ Ethernet:
✑ Transport Layer: This layer is responsible for providing communication services directly to the application processes running on different hosts. TCP is a core protocol in this layer.
✑ Internetwork Layer: This layer is responsible for logical addressing, routing, and
packet forwarding. IP is the primary protocol for this layer.
✑ Application Layer: This layer interfaces directly with application processes and provides common network services. FTP is an example of a protocol operating in this layer.
✑ Network Layer: In the TCP/IP model, this layer includes both the data link and physical layers of the OSI model. Ethernet is a protocol used in this layer to define network standards and communication protocols at the data link and physical levels.
References:
✑ TCP/IP Model Overview: Cisco TCP/IP Model
✑ Understanding the TCP/IP Model: TCP/IP Layers
Does this meet the goal?
Correct Answer:A
Question 6
Which two statements are true about the IPv4 address of the default gateway configured on a host? (Choose 2.)
Note: You will receive partial credit for each correct selection.
Correct Answer:BD
•Statement B: "The same default gateway IPv4 address is configured on each host on the local network." This is true because all hosts on the same local network (subnet) use the same default gateway IP address to send packets destined for other networks.
•Statement D: "The default gateway is the IPv4 address of the router interface connected to the same local network as the host." This is true because the default gateway is the IP address of the router's interface that is directly connected to the local network.
•Statement A: "The IPv4 address of the default gateway must be the first host address in the subnet." This is not necessarily true. The default gateway can be any address within the subnet range.
•Statement C: "The default gateway is the Loopback0 interface IPv4 address of the router connected to the same local network as the host." This is not true; the default gateway is the IP address of the router's physical or logical interface connected to the local network.
•Statement E: "Hosts learn the default gateway IPv4 address through router advertisement messages." This is generally true for IPv6 with Router Advertisement (RA) messages, but not typically how IPv4 hosts learn the default gateway address.
References:
•Cisco Default Gateway Configuration: Cisco Default Gateway